4 Dyslexia Myths That Can Confuse Parents
Written by Sandie Barrie Blackley, Speech-Language Pathologist
Published on June 1, 2025
As Lexercise therapists communicate with the families of children with dyslexia, they are continually impressed by the amount of research parents have done. Getting a dyslexia diagnosis for their child and then finding the right treatment for a student with learning differences is never simple.
At the same time, Lexercise therapists express their surprise and concern at the prevailing myths and misunderstandings surrounding dyslexia. Thanks to these myths, some parents may even be persuaded that their child’s learning difficulties are not treatable. As you try to support your child with dyslexia, take a moment to review our guide to the most common dyslexia myths.
Dyslexia Myth Infographic
If you want a quick overview of the four primary myths about dyslexia, review our infographic below:
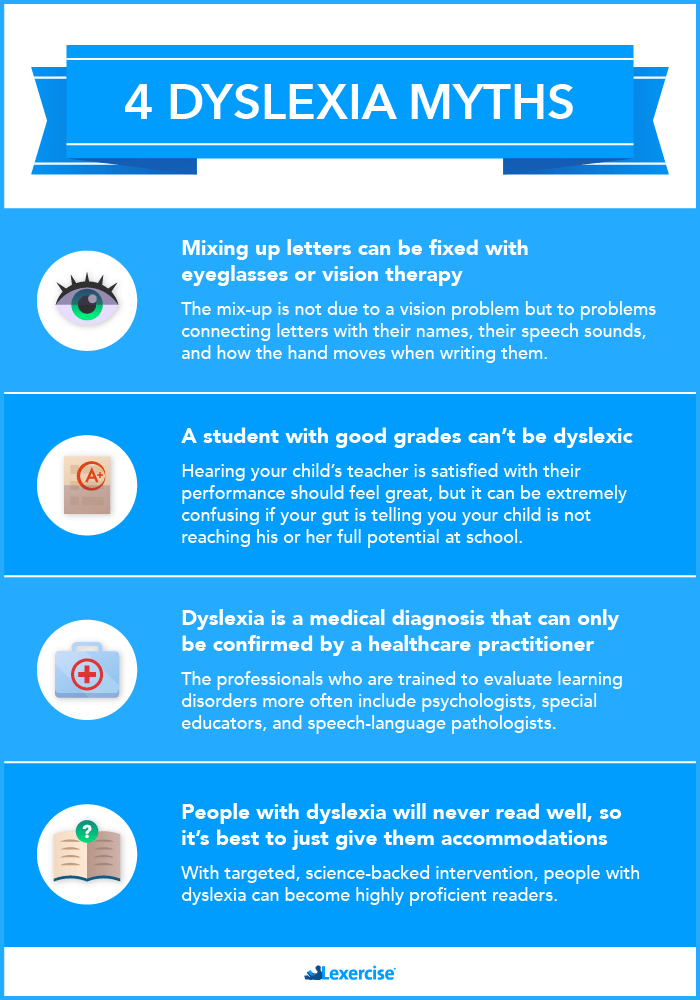
Debunking The Most Common Misconceptions About Dyslexia
If you’re interested in learning more about Dyslexia facts and myths, check out the following four most common misconceptions about dyslexia:
MYTH #1: Dyslexia Causes People to See Words and Letters Backward
In 1925, Dr. Samuel Orton used the term strephosymbolia, literally reversed symbols, in explaining why some people have great trouble reading despite adequate intelligence. A decade later, Orton said that he thought the main problem was actually in “the process of synthesizing the word as a spoken unit from its component sounds.” (See What is Orton-Gillingham and How Does it Treat Dyslexia?)
Since the 1970s, with modern neuroscience technologies, it has become clear that most dyslexics do not have difficulties with vision or visual perception. Instead, most people with dyslexia have difficulties with processing speech sounds.
Still, the old idea that dyslexics see things backward or reversed has persisted and become a popular myth.
Some recent research suggests that a minority of struggling readers may have difficulty with some aspects of vision, such as visual spatial attention. In his book, Reading in the Brain: the New Science of How We Read, French neuroscientist Dr. Stanislas Dehaene sums up the current science: “…brain imaging supports the claim that the crux of the problem often lies at the interface between vision and speech….” For more information, see a related post by Dr. William O. Young, Five Ways Not to Treat Dyslexia.
MYTH #2: Students Who Make Good Grades Must Not Have Dyslexia
Good grades do not rule out dyslexia! We are going to address common concerns about grade level in an upcoming post, but meanwhile, see 5 Reasons Why Good Grades Don’t Rule Out Dyslexia.
MYTH #3: Dyslexia is a Medical Diagnosis That Can Only Be Used by a Healthcare Practitioner
Learning disorders, including dyslexia, have well-documented lifelong negative effects on health and well-being, especially when treatment is withheld or delayed. But a learning disorder like dyslexia is not considered a medical diagnosis, nor, in most cases, is the treatment for dyslexia covered by medical insurance.
Neither the World Health Organization’s International Classification of Diseases, 11th Edition (ICD-11) nor the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, has a specific classification code for dyslexia. Instead, both include reading disorders under a broader category of learning disorders.
Physicians and other medical providers are typically not trained in how to evaluate learning disorders like dyslexia. The exception might be some developmental pediatricians, who have additional training in cognition and learning. The professionals who are trained to evaluate learning disorders more often include psychologists, special educators, and speech-language pathologists. See Who is Qualified to Make a Dyslexia Diagnosis?
MYTH #4: People With Dyslexia Will Never Read Well, So It’s Best to Just Give Them Accommodations and Other Ways to Compensate.
With targeted, science-backed intervention, people with dyslexia can become highly proficient readers. In conjunction with appropriate intervention, accommodations and technologies can certainly play a role in reducing fatigue and improving academic performance (see The Limits of Reading Accommodations).
It is the appropriate intervention–consistent, targeted therapy plus consistent daily practice–that turns struggling students into confident readers.
Frequently Asked Questions About Dyslexia
Still have questions about dyslexia? Review our answers to some of the most frequently asked questions about dyslexia below:
What Age Is Dyslexia Diagnosed?
While symptoms of dyslexia can be observed earlier than elementary school, dyslexia is usually diagnosed around the age of seven or eight (typically, at the end of second grade or the beginning of third grade). However, it’s often better to start testing a child five years old or older after they’ve received at least six months of reading instruction.
Testing early helps students receive the treatment they need as soon as possible. This approach can reduce difficulties in school, increase the level of support a student receives, and improve reading skills.
Can You Outgrow Dyslexia? Will Dyslexia Go Away?
Another common myth about dyslexia is that you’ll eventually outgrow it. Dyslexia is a lifelong condition and can’t be cured.
While dyslexia won’t go away, a number of treatment options are available to help students better manage their dyslexia. For example, structured literacy programs, coping strategies, and technology can all help treat dyslexia.
Does Dyslexia Get Worse With Age?
Dyslexia doesn’t “get worse” with age, but the difficulties it causes may feel more impactful as someone gets older. For example, if someone has untreated dyslexia, middle school will likely feel far more difficult than elementary school due to the more advanced reading requirements.
Receiving treatment earlier for dyslexia helps prevent the perception that dyslexia is getting worse. Instead of feeling overwhelmed by a more difficult reading or writing task, a student will have developed the skills and coping strategies to make them feel confident and ready for the challenge.
Can You Be Dyslexic With Numbers and Not Letters?
Dyslexia only refers to difficulties processing letters and words. However, if you do struggle with numbers, you may have dyscalculia, which is a learning disorder that affects a person’s ability to do math.
Choose Lexercise for Evidence-Backed Dyslexia Testing and Treatment
As a literacy platform designed to give struggling readers and writers access to excellent, evidence-based structural literacy, Lexercise can help your child receive testing and treatment for dyslexia. Our science-based curriculum employs the most up-to-date methodologies to ensure treatment is effective. Since we offer online dyslexia programs, your child can receive expert instruction from the comfort of your home and at a time that works best for your family.
Learn more about our online dyslexia treatment services today. To find out more about myth-busting dyslexia research, contact Lexercise today.
Improve Your Child’s Reading
Learn more about Lexercise today.
Schedule a FREE
15-minute consultation


